
Unfortunately, digital crime is an everyday reality. We have created this page to be clear on our position and share information with you about common types of scams; real-life situations that we have seen as part of digital collaboration with our customers and business partners.
Many of the scams want to make you pay to the imposter’s bank account.
Enza Zaden will never ask you to change its bank details over e-mail or phone. Such changes will be sent to you in a separate written statement, on paper. You must verify any change with your Enza Zaden representative by phone, on a phone number that was previously known to you.
It is important to report anything unusual to us. This allows us to work with you to reduce the impact, warn others and raise awareness.
Please report to security@enzazaden.com Always include suspicious e-mail messages as an attachment, as this contains the source information that is needed to analyze it.
A cybercriminal sends you messages that seem to come from Enza Zaden. They could inquire about payment status or outstanding amounts. If you respond to the message, they will ask you to transfer money to a new bank account, claiming bank issues. They may use an Enza Zaden e-mail address in the so-called display name. However, the message display name is just a line of text where the sender can put in anything. Alternatively, a domain is used that mimics legitimate Enza Zaden domains; i.e. enzazadden.com instead of enzazaden.com.
Using business details can make these messages convincing. Business details could come from your and our websites or public sources such as LinkedIn.
Example of a false message
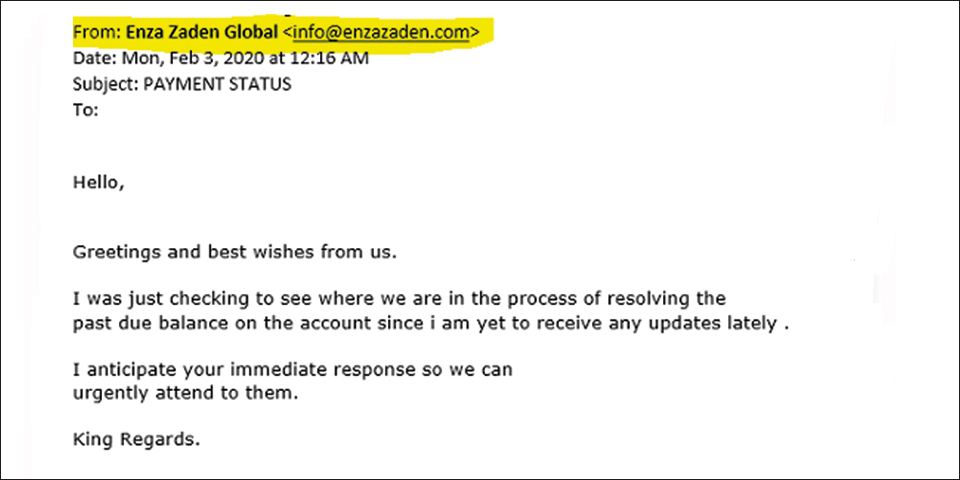
If the display name is used to impersonate an Enza Zaden address, the reply address usually reveals the real sender address. After all, the imposter will want to receive your response.
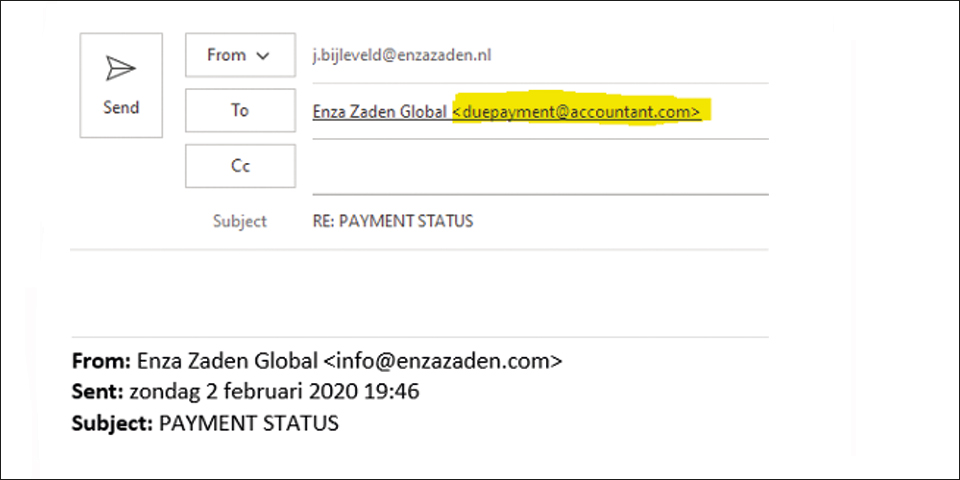
In the message below the imposter used @enzazaden.ml (ML instead of NL)

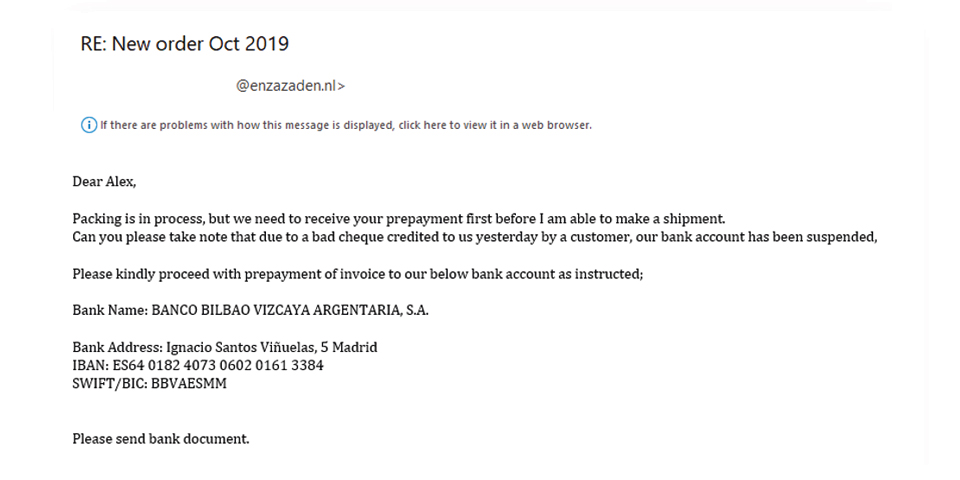
We have seen cases were a computer virus/malware was able to hijack an e-mail conversation between an Enza Zaden employee and the customer and insert or add to a message. The hacker attempted to convince the customer to pay to a different bank account.
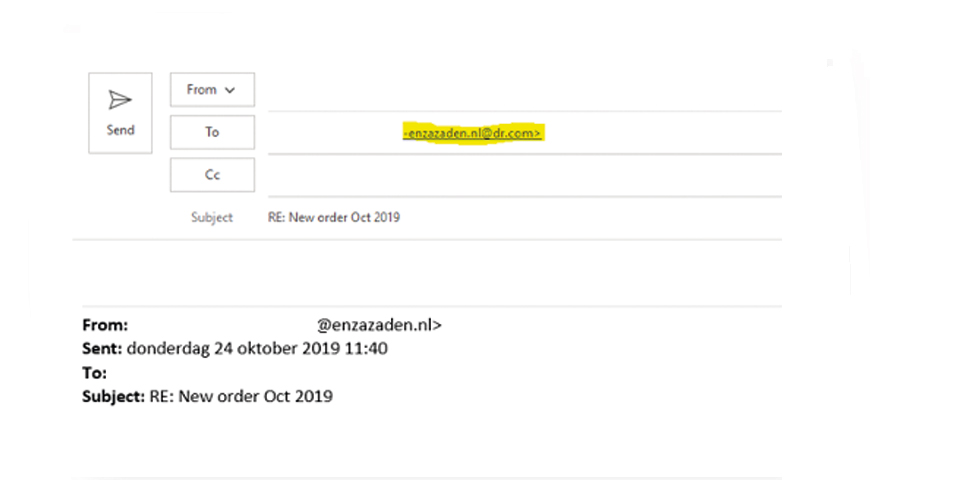
Example of a false message
A reply to the message reveals a different address
A customer received an invoice were the Enza Zaden bank information was blanked out and new instructions were added to the footer.

Enza Zaden uses all common technical e-mail security standards to allow you to determine the legitimacy of a message:
Please contact your IT or e-mail provider on how to have your e-mail system check for e-mail authenticity marks.
The US government cyber security agency has useful guidance that could help to get you organized. The cyber security essentials guide provides a good basic overview.
The NIST Cyber security framework provides a profound approach to cyber security.